Table of Contents
- 1. How to Include Spring Cloud Gateway
- 2. Glossary
- 3. How It Works
- 4. Route Predicate Factories
- 4.1. After Route Predicate Factory
- 4.2. Before Route Predicate Factory
- 4.3. Between Route Predicate Factory
- 4.4. Cookie Route Predicate Factory
- 4.5. Header Route Predicate Factory
- 4.6. Host Route Predicate Factory
- 4.7. Method Route Predicate Factory
- 4.8. Path Route Predicate Factory
- 4.9. Query Route Predicate Factory
- 4.10. RemoteAddr Route Predicate Factory
- 5. GatewayFilter Factories
- 5.1. AddRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.2. AddRequestParameter GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.3. AddResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.4. Hystrix GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.5. PrefixPath GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.6. PreserveHostHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.7. RequestRateLimiter GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.8. RedirectTo GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.9. RemoveHopByHopHeadersFilter GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.10. RemoveRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.11. RemoveResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.12. RewritePath GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.13. RewriteResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.14. SaveSession GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.15. SecureHeaders GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.16. SetPath GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.17. SetResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.18. SetStatus GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.19. StripPrefix GatewayFilter Factory
- 5.20. Retry GatewayFilter Factory
- 6. Global Filters
- 7. TLS / SSL
- 8. Configuration
- 9. CORS Configuration
- 10. Actuator API
- 11. Developer Guide
- 12. Building a Simple Gateway Using Spring MVC or Webflux
2.0.3.RELEASE
This project provides an API Gateway built on top of the Spring Ecosystem, including: Spring 5, Spring Boot 2 and Project Reactor. Spring Cloud Gateway aims to provide a simple, yet effective way to route to APIs and provide cross cutting concerns to them such as: security, monitoring/metrics, and resiliency.
To include Spring Cloud Gateway in your project use the starter with group org.springframework.cloud
and artifact id spring-cloud-starter-gateway. See the Spring Cloud Project page
for details on setting up your build system with the current Spring Cloud Release Train.
If you include the starter, but, for some reason, you do not want the gateway to be enabled, set spring.cloud.gateway.enabled=false.
![[Important]](images/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Spring Cloud Gateway requires the Netty runtime provided by Spring Boot and Spring Webflux. It does not work in a traditional Servlet Container or built as a WAR. |
- Route: Route the basic building block of the gateway. It is defined by an ID, a destination URI, a collection of predicates and a collection of filters. A route is matched if aggregate predicate is true.
- Predicate: This is a Java 8 Function Predicate. The input type is a Spring Framework
ServerWebExchange. This allows developers to match on anything from the HTTP request, such as headers or parameters. - Filter: These are instances Spring Framework
GatewayFilterconstructed in with a specific factory. Here, requests and responses can be modified before or after sending the downstream request.
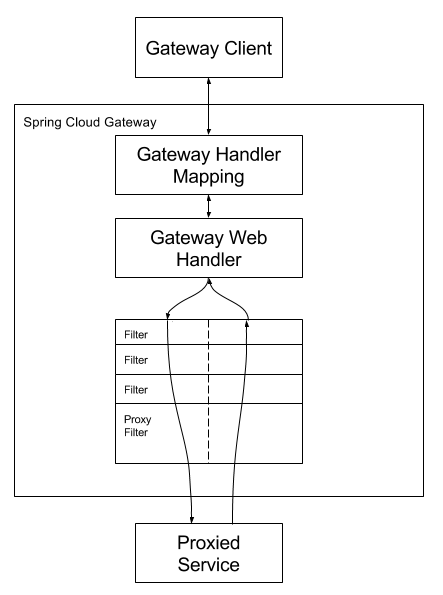
Clients make requests to Spring Cloud Gateway. If the Gateway Handler Mapping determines that a request matches a Route, it is sent to the Gateway Web Handler. This handler runs sends the request through a filter chain that is specific to the request. The reason the filters are divided by the dotted line, is that filters may execute logic before the proxy request is sent or after. All "pre" filter logic is executed, then the proxy request is made. After the proxy request is made, the "post" filter logic is executed.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
URIs defined in routes without a port will get a default port set to 80 and 443 for HTTP and HTTPS URIs respectively. |
Spring Cloud Gateway matches routes as part of the Spring WebFlux HandlerMapping infrastructure. Spring Cloud Gateway includes many built-in Route Predicate Factories. All of these predicates match on different attributes of the HTTP request. Multiple Route Predicate Factories can be combined and are combined via logical and.
The After Route Predicate Factory takes one parameter, a datetime. This predicate matches requests that happen after the current datetime.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: after_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - After=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
This route matches any request after Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver).
The Before Route Predicate Factory takes one parameter, a datetime. This predicate matches requests that happen before the current datetime.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: before_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Before=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
This route matches any request before Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver).
The Between Route Predicate Factory takes two parameters, datetime1 and datetime2. This predicate matches requests that happen after datetime1 and before datetime2. The datetime2 parameter must be after datetime1.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: between_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Between=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver], 2017-01-21T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
This route matches any request after Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver) and before Jan 21, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver). This could be useful for maintenance windows.
The Cookie Route Predicate Factory takes two parameters, the cookie name and a regular expression. This predicate matches cookies that have the given name and the value matches the regular expression.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: cookie_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Cookie=chocolate, ch.p
This route matches the request has a cookie named chocolate who’s value matches the ch.p regular expression.
The Header Route Predicate Factory takes two parameters, the header name and a regular expression. This predicate matches with a header that has the given name and the value matches the regular expression.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: header_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Header=X-Request-Id, \d+
This route matches if the request has a header named X-Request-Id whos value matches the \d+ regular expression (has a value of one or more digits).
The Host Route Predicate Factory takes one parameter: the host name pattern. The pattern is an Ant style pattern with . as the separator. This predicates matches the Host header that matches the pattern.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: host_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Host={sub}.somehost.org
Ant patterns work as well, such as **.somehost.org.
This route would match if the request has a Host header has the value www.somehost.org or beta.somehost.org.
This predicate extracts the URI template variables (like sub defined in the example above) as a map of names and values and places it in the ServerWebExchange.getAttributes() with a key defined in ServerWebExchangeUtils.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE. Those values are then available for use by GatewayFilter Factories
The Method Route Predicate Factory takes one parameter: the HTTP method to match.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: method_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Method=GET
This route would match if the request method was a GET.
The Path Route Predicate Factory takes one parameter: a Spring PathMatcher pattern.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: host_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Path=/foo/{segment}
This route would match if the request path was, for example: /foo/1 or /foo/bar.
This predicate extracts the URI template variables (like segment defined in the example above) as a map of names and values and places it in the ServerWebExchange.getAttributes() with a key defined in ServerWebExchangeUtils.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE. Those values are then available for use by GatewayFilter Factories
A utility method is available to make access to these variables easier.
Map<String, String> uriVariables = ServerWebExchangeUtils.getPathPredicateVariables(exchange);
String segment = uriVariables.get("segment");The Query Route Predicate Factory takes two parameters: a required param and an optional regexp.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: query_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Query=baz
This route would match if the request contained a baz query parameter.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: query_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Query=foo, ba.
This route would match if the request contained a foo query parameter whose value matched the ba. regexp, so bar and baz would match.
The RemoteAddr Route Predicate Factory takes a list (min size 1) of CIDR-notation (IPv4 or IPv6) strings, e.g. 192.168.0.1/16 (where 192.168.0.1 is an IP address and 16 is a subnet mask).
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: remoteaddr_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - RemoteAddr=192.168.1.1/24
This route would match if the remote address of the request was, for example, 192.168.1.10.
By default the RemoteAddr Route Predicate Factory uses the remote address from the incoming request. This may not match the actual client IP address if Spring Cloud Gateway sits behind a proxy layer.
You can customize the way that the remote address is resolved by setting a custom RemoteAddressResolver.
Spring Cloud Gateway comes with one non-default remote address resolver which is based off of the X-Forwarded-For header, XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver.
XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver has two static constructor methods which take different approaches to security:
XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver::trustAll returns a RemoteAddressResolver which always takes the first IP address found in the X-Forwarded-For header.
This approach is vulnerable to spoofing, as a malicious client could set an initial value for the X-Forwarded-For which would be accepted by the resolver.
XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver::maxTrustedIndex takes an index which correlates to the number of trusted infrastructure running in front of Spring Cloud Gateway.
If Spring Cloud Gateway is, for example only accessible via HAProxy, then a value of 1 should be used.
If two hops of trusted infrastructure are required before Spring Cloud Gateway is accessible, then a value of 2 should be used.
Given the following header value:
X-Forwarded-For: 0.0.0.1, 0.0.0.2, 0.0.0.3
The maxTrustedIndex values below will yield the following remote addresses.
maxTrustedIndex | result |
|---|---|
[ | (invalid, |
1 | 0.0.0.3 |
2 | 0.0.0.2 |
3 | 0.0.0.1 |
[4, | 0.0.0.1 |
GatewayConfig.java
RemoteAddressResolver resolver = XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver
.maxTrustedIndex(1);
...
.route("direct-route",
r -> r.remoteAddr("10.1.1.1", "10.10.1.1/24")
.uri("https://downstream1")
.route("proxied-route",
r -> r.remoteAddr(resolver, "10.10.1.1", "10.10.1.1/24")
.uri("https://downstream2")
)Route filters allow the modification of the incoming HTTP request or outgoing HTTP response in some manner. Route filters are scoped to a particular route. Spring Cloud Gateway includes many built-in GatewayFilter Factories.
NOTE For more detailed examples on how to use any of the following filters, take a look at the unit tests.
The AddRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory takes a name and value parameter.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: add_request_header_route uri: http://example.org filters: - AddRequestHeader=X-Request-Foo, Bar
This will add X-Request-Foo:Bar header to the downstream request’s headers for all matching requests.
The AddRequestParameter GatewayFilter Factory takes a name and value parameter.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: add_request_parameter_route uri: http://example.org filters: - AddRequestParameter=foo, bar
This will add foo=bar to the downstream request’s query string for all matching requests.
The AddResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory takes a name and value parameter.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: add_request_header_route uri: http://example.org filters: - AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo, Bar
This will add X-Response-Foo:Bar header to the downstream response’s headers for all matching requests.
Hystrix is a library from Netflix that implements the circuit breaker pattern. The Hystrix GatewayFilter allows you to introduce circuit breakers to your gateway routes, protecting your services from cascading failures and allowing you to provide fallback responses in the event of downstream failures.
To enable Hystrix GatewayFilters in your project, add a dependency on spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix from Spring Cloud Netflix.
The Hystrix GatewayFilter Factory requires a single name parameter, which is the name of the HystrixCommand.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: hystrix_route uri: http://example.org filters: - Hystrix=myCommandName
This wraps the remaining filters in a HystrixCommand with command name myCommandName.
The Hystrix filter can also accept an optional fallbackUri parameter. Currently, only forward: schemed URIs are supported. If the fallback is called, the request will be forwarded to the controller matched by the URI.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: hystrix_route uri: lb://backing-service:8088 predicates: - Path=/consumingserviceendpoint filters: - name: Hystrix args: name: fallbackcmd fallbackUri: forward:/incaseoffailureusethis - RewritePath=/consumingserviceendpoint, /backingserviceendpoint
This will forward to the /incaseoffailureusethis URI when the Hystrix fallback is called. Note that this example also demonstrates (optional) Spring Cloud Netflix Ribbon load-balancing via the lb prefix on the destination URI.
Hystrix settings (such as timeouts) can be configured with global defaults or on a route by route basis using application properties as explained on the Hystrix wiki.
To set a 5 second timeout for the example route above, the following configuration would be used:
application.yml.
hystrix.command.fallbackcmd.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds: 5000
The PrefixPath GatewayFilter Factory takes a single prefix parameter.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: prefixpath_route uri: http://example.org filters: - PrefixPath=/mypath
This will prefix /mypath to the path of all matching requests. So a request to /hello, would be sent to /mypath/hello.
The PreserveHostHeader GatewayFilter Factory has not parameters. This filter, sets a request attribute that the routing filter will inspect to determine if the original host header should be sent, rather than the host header determined by the http client.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: preserve_host_route uri: http://example.org filters: - PreserveHostHeader
The RequestRateLimiter GatewayFilter Factory is uses a RateLimiter implementation to determine if the current request is allowed to proceed. If it is not, a status of HTTP 429 - Too Many Requests (by default) is returned.
This filter takes an optional keyResolver parameter and parameters specific to the rate limiter (see below).
keyResolver is a bean that implements the KeyResolver interface. In configuration, reference the bean by name using SpEL. #{@myKeyResolver} is a SpEL expression referencing a bean with the name myKeyResolver.
KeyResolver.java.
public interface KeyResolver { Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange); }
The KeyResolver interface allows pluggable strategies to derive the key for limiting requests. In future milestones, there will be some KeyResolver implementations.
The default implementation of KeyResolver is the PrincipalNameKeyResolver which retrieves the Principal from the ServerWebExchange and calls Principal.getName().
By default, if the KeyResolver does not find a key, requests will be denied. This behavior can be adjust with the spring.cloud.gateway.filter.request-rate-limiter.deny-empty-key (true or false) and spring.cloud.gateway.filter.request-rate-limiter.empty-key-status-code properties.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The RequestRateLimiter is not configurable via the "shortcut" notation. The example below is invalid |
application.properties.
# INVALID SHORTCUT CONFIGURATION
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].filters[0]=RequestRateLimiter=2, 2, #{@userkeyresolver}
The redis implementation is based off of work done at Stripe. It requires the use of the spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive Spring Boot starter.
The algorithm used is the Token Bucket Algorithm.
The redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate is how many requests per second do you want a user to be allowed to do, without any dropped requests. This is the rate that the token bucket is filled.
The redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity is the maximum number of requests a user is allowed to do in a single second. This is the number of tokens the token bucket can hold. Setting this value to zero will block all requests.
A steady rate is accomplished by setting the same value in replenishRate and burstCapacity. Temporary bursts can be allowed by setting burstCapacity higher than replenishRate. In this case, the rate limiter needs to be allowed some time between bursts (according to replenishRate), as 2 consecutive bursts will result in dropped requests (HTTP 429 - Too Many Requests).
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: requestratelimiter_route uri: http://example.org filters: - name: RequestRateLimiter args: redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 10 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 20
Config.java.
@Bean KeyResolver userKeyResolver() { return exchange -> Mono.just(exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("user")); }
This defines a request rate limit of 10 per user. A burst of 20 is allowed, but the next second only 10 requests will be available. The KeyResolver is a simple one that gets the user request parameter (note: this is not recommended for production).
A rate limiter can also be defined as a bean implementing the RateLimiter interface. In configuration, reference the bean by name using SpEL. #{@myRateLimiter} is a SpEL expression referencing a bean with the name myRateLimiter.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: requestratelimiter_route uri: http://example.org filters: - name: RequestRateLimiter args: rate-limiter: "#{@myRateLimiter}" key-resolver: "#{@userKeyResolver}"
The RedirectTo GatewayFilter Factory takes a status and a url parameter. The status should be a 300 series redirect http code, such as 301. The url should be a valid url. This will be the value of the Location header.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: prefixpath_route uri: http://example.org filters: - RedirectTo=302, http://acme.org
This will send a status 302 with a Location:http://acme.org header to perform a redirect.
The RemoveHopByHopHeadersFilter GatewayFilter Factory removes headers from forwarded requests. The default list of headers that is removed comes from the IETF.
The default removed headers are:
- Connection
- Keep-Alive
- Proxy-Authenticate
- Proxy-Authorization
- TE
- Trailer
- Transfer-Encoding
- Upgrade
To change this, set the spring.cloud.gateway.filter.remove-non-proxy-headers.headers property to the list of header names to remove.
The RemoveRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory takes a name parameter. It is the name of the header to be removed.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: removerequestheader_route uri: http://example.org filters: - RemoveRequestHeader=X-Request-Foo
This will remove the X-Request-Foo header before it is sent downstream.
The RemoveResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory takes a name parameter. It is the name of the header to be removed.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: removeresponseheader_route uri: http://example.org filters: - RemoveResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo
This will remove the X-Response-Foo header from the response before it is returned to the gateway client.
The RewritePath GatewayFilter Factory takes a path regexp parameter and a replacement parameter. This uses Java regular expressions for a flexible way to rewrite the request path.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: rewritepath_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Path=/foo/** filters: - RewritePath=/foo/(?<segment>.*), /$\{segment}
For a request path of /foo/bar, this will set the path to /bar before making the downstream request. Notice the $\ which is replaced with $ because of the YAML spec.
The RewriteResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory takes name, regexp, and replacement parameters. It uses Java regular expressions for a flexible way to rewrite the response header value.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: rewriteresponseheader_route uri: http://example.org filters: - RewriteResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo, , password=[^&]+, password=***
For a header value of /42?user=ford&password=omg!what&flag=true, it will be set to /42?user=ford&password=***&flag=true after making the downstream request. Please use $\ to mean $ because of the YAML spec.
The SaveSession GatewayFilter Factory forces a WebSession::save operation before forwarding the call downstream. This is of particular use when
using something like Spring Session with a lazy data store and need to ensure the session state has been saved before making the forwarded call.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: save_session uri: http://example.org predicates: - Path=/foo/** filters: - SaveSession
If you are integrating Spring Security with Spring Session, and want to ensure security details have been forwarded to the remote process, this is critical.
The SecureHeaders GatewayFilter Factory adds a number of headers to the response at the reccomendation from this blog post.
The following headers are added (allong with default values):
X-Xss-Protection:1; mode=blockStrict-Transport-Security:max-age=631138519X-Frame-Options:DENYX-Content-Type-Options:nosniffReferrer-Policy:no-referrerContent-Security-Policy:default-src 'self' https:; font-src 'self' https: data:; img-src 'self' https: data:; object-src 'none'; script-src https:; style-src 'self' https: 'unsafe-inline'X-Download-Options:noopenX-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies:none
To change the default values set the appropriate property in the spring.cloud.gateway.filter.secure-headers namespace:
Property to change:
xss-protection-headerstrict-transport-securityframe-optionscontent-type-optionsreferrer-policycontent-security-policydownload-optionspermitted-cross-domain-policies
The SetPath GatewayFilter Factory takes a path template parameter. It offers a simple way to manipulate the request path by allowing templated segments of the path. This uses the uri templates from Spring Framework. Multiple matching segments are allowed.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: setpath_route uri: http://example.org predicates: - Path=/foo/{segment} filters: - SetPath=/{segment}
For a request path of /foo/bar, this will set the path to /bar before making the downstream request.
The SetResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory takes name and value parameters.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: setresponseheader_route uri: http://example.org filters: - SetResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo, Bar
This GatewayFilter replaces all headers with the given name, rather than adding. So if the downstream server responded with a X-Response-Foo:1234, this would be replaced with X-Response-Foo:Bar, which is what the gateway client would receive.
The SetStatus GatewayFilter Factory takes a single status parameter. It must be a valid Spring HttpStatus. It may be the integer value 404 or the string representation of the enumeration NOT_FOUND.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: setstatusstring_route uri: http://example.org filters: - SetStatus=BAD_REQUEST - id: setstatusint_route uri: http://example.org filters: - SetStatus=401
In either case, the HTTP status of the response will be set to 401.
The StripPrefix GatewayFilter Factory takes one paramter, parts. The parts parameter indicated the number of parts in the path to strip from the request before sending it downstream.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: nameRoot uri: http://nameservice predicates: - Path=/name/** filters: - StripPrefix=2
When a request is made through the gateway to /name/bar/foo the request made to nameservice will look like http://nameservice/foo.
The Retry GatewayFilter Factory takes retries, statuses, methods, and series as parameters.
retries: the number of retries that should be attemptedstatuses: the HTTP status codes that should be retried, represented usingorg.springframework.http.HttpStatusmethods: the HTTP methods that should be retried, represented usingorg.springframework.http.HttpMethodseries: the series of status codes to be retried, represented usingorg.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: retry_test uri: http://localhost:8080/flakey predicates: - Host=*.retry.com filters: - name: Retry args: retries: 3 statuses: BAD_GATEWAY
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
When using the retry filter with a |
The GlobalFilter interface has the same signature as GatewayFilter. These are special filters that are conditionally applied to all routes. (This interface and usage are subject to change in future milestones).
When a request comes in (and matches a Route) the Filtering Web Handler will add all instances of GlobalFilter and all route specific instances of GatewayFilter to a filter chain. This combined filter chain is sorted by the org.springframework.core.Ordered interface, which can be set by implementing the getOrder() method or by using the @Order annotation.
As Spring Cloud Gateway distinguishes between "pre" and "post" phases for filter logic execution (see: How It Works), the filter with the highest precedence will be the first in the "pre"-phase and the last in the "post"-phase.
ExampleConfiguration.java.
@Bean @Order(-1) public GlobalFilter a() { return (exchange, chain) -> { log.info("first pre filter"); return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { log.info("third post filter"); })); }; } @Bean @Order(0) public GlobalFilter b() { return (exchange, chain) -> { log.info("second pre filter"); return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { log.info("second post filter"); })); }; } @Bean @Order(1) public GlobalFilter c() { return (exchange, chain) -> { log.info("third pre filter"); return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { log.info("first post filter"); })); }; }
The ForwardRoutingFilter looks for a URI in the exchange attribute ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR. If the url has a forward scheme (ie forward:///localendpoint), it will use the Spring DispatcherHandler to handler the request. The path part of the request URL will be overridden with the path in the forward URL. The unmodified original url is appended to the list in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_ORIGINAL_REQUEST_URL_ATTR attribute.
The LoadBalancerClientFilter looks for a URI in the exchange attribute ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR. If the url has a lb scheme (ie lb://myservice), it will use the Spring Cloud LoadBalancerClient to resolve the name (myservice in the previous example) to an actual host and port and replace the URI in the same attribute. The unmodified original url is appended to the list in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_ORIGINAL_REQUEST_URL_ATTR attribute. The filter will also look in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_SCHEME_PREFIX_ATTR attribute to see if it equals lb and then the same rules apply.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: myRoute uri: lb://service predicates: - Path=/service/**
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The |
The Netty Routing Filter runs if the url located in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR exchange attribute has a http or https scheme. It uses the Netty HttpClient to make the downstream proxy request. The response is put in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR exchange attribute for use in a later filter. (There is an experimental WebClientHttpRoutingFilter that performs the same function, but does not require netty)
The NettyWriteResponseFilter runs if there is a Netty HttpClientResponse in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR exchange attribute. It is run after all other filters have completed and writes the proxy response back to the gateway client response. (There is an experimental WebClientWriteResponseFilter that performs the same function, but does not require netty)
The RouteToRequestUrlFilter runs if there is a Route object in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR exchange attribute. It creates a new URI, based off of the request URI, but updated with the URI attribute of the Route object. The new URI is placed in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR exchange attribute`.
If the URI has a scheme prefix, such as lb:ws://serviceid, the lb scheme is stripped from the URI and placed in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_SCHEME_PREFIX_ATTR for use later in the filter chain.
The Websocket Routing Filter runs if the url located in the ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR exchange attribute has a ws or wss scheme. It uses the Spring Web Socket infrastructure to forward the Websocket request downstream.
Websockets may be load-balanced by prefixing the URI with lb, such as lb:ws://serviceid.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If you are using SockJS as a fallback over normal http, you should configure a normal HTTP route as well as the Websocket Route. |
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: # SockJS route - id: websocket_sockjs_route uri: http://localhost:3001 predicates: - Path=/websocket/info/** # Normwal Websocket route - id: websocket_route uri: ws://localhost:3001 predicates: - Path=/websocket/**
To enable Gateway Metrics add spring-boot-starter-actuator as a project dependency. Then, by default, the Gateway Metrics Filter runs as long as the property spring.cloud.gateway.metrics.enabled is not set to false. This filter adds a timer metric named "gateway.requests" with the following tags:
routeId: The route idrouteUri: The URI that the API will be routed tooutcome: Outcome as classified by HttpStatus.Seriesstatus: Http Status of the request returned to the client
These metrics are then available to be scraped from /actuator/metrics/gateway.requests and can be easily integated with Prometheus to create a Grafana dashboard.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
To enable the pometheus endpoint add micrometer-registry-prometheus as a project dependency. |
After the Gateway has routed a ServerWebExchange it will mark that exchange as "routed" by adding gatewayAlreadyRouted
to the exchange attributes. Once a request has been marked as routed, other routing filters will not route the request again,
essentially skipping the filter. There are convenience methods that you can use to mark an exchange as routed
or check if an exchange has already been routed.
ServerWebExchangeUtils.isAlreadyRoutedtakes aServerWebExchangeobject and checks if it has been "routed"ServerWebExchangeUtils.setAlreadyRoutedtakes aServerWebExchangeobject and marks it as "routed"
The Gateway can listen for requests on https by following the usual Spring server configuration. Example:
application.yml.
server: ssl: enabled: true key-alias: scg key-store-password: scg1234 key-store: classpath:scg-keystore.p12 key-store-type: PKCS12
Gateway routes can be routed to both http and https backends. If routing to a https backend then the Gateway can be configured to trust all downstream certificates with the following configuration:
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: httpclient: ssl: useInsecureTrustManager: true
Using an insecure trust manager is not suitable for production. For a production deployment the Gateway can be configured with a set of known certificates that it can trust with the follwing configuration:
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: httpclient: ssl: trustedX509Certificates: - cert1.pem - cert2.pem
If the Spring Cloud Gateway is not provisioned with trusted certificates the default trust store is used (which can be overriden with system property javax.net.ssl.trustStore).
The Gateway maintains a client pool that it uses to route to backends. When communicating over https the client initiates a TLS handshake. A number of timeouts are assoicated with this handshake. These timeouts can be configured (defaults shown):
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: httpclient: ssl: handshake-timeout-millis: 10000 close-notify-flush-timeout-millis: 3000 close-notify-read-timeout-millis: 0
Configuration for Spring Cloud Gateway is driven by a collection of `RouteDefinitionLocator`s.
RouteDefinitionLocator.java.
public interface RouteDefinitionLocator { Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions(); }
By default, a PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator loads properties using Spring Boot’s @ConfigurationProperties mechanism.
The configuration examples above all use a shortcut notation that uses positional arguments rather than named ones. The two examples below are equivalent:
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: setstatus_route uri: http://example.org filters: - name: SetStatus args: status: 401 - id: setstatusshortcut_route uri: http://example.org filters: - SetStatus=401
For some usages of the gateway, properties will be adequate, but some production use cases will benefit from loading configuration from an external source, such as a database. Future milestone versions will have RouteDefinitionLocator implementations based off of Spring Data Repositories such as: Redis, MongoDB and Cassandra.
To allow for simple configuration in Java, there is a fluent API defined in the RouteLocatorBuilder bean.
GatewaySampleApplication.java.
// static imports from GatewayFilters and RoutePredicates @Bean public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder, ThrottleGatewayFilterFactory throttle) { return builder.routes() .route(r -> r.host("**.abc.org").and().path("/image/png") .filters(f -> f.addResponseHeader("X-TestHeader", "foobar")) .uri("http://httpbin.org:80") ) .route(r -> r.path("/image/webp") .filters(f -> f.addResponseHeader("X-AnotherHeader", "baz")) .uri("http://httpbin.org:80") ) .route(r -> r.order(-1) .host("**.throttle.org").and().path("/get") .filters(f -> f.filter(throttle.apply(1, 1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS))) .uri("http://httpbin.org:80") ) .build(); }
This style also allows for more custom predicate assertions. The predicates defined by RouteDefinitionLocator beans are combined using logical and. By using the fluent Java API, you can use the and(), or() and negate() operators on the Predicate class.
The Gateway can be configured to create routes based on services registered with a DiscoveryClient compatible service registry.
To enable this, set spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.enabled=true and make sure a DiscoveryClient implementation is on the classpath and enabled (such as Netflix Eureka, Consul or Zookeeper).
By default the Gateway defines a single predicate and filter for routes created via a DiscoveryClient.
The default predicate is a path predicate defined with the pattern /serviceId/**, where serviceId is
the id of the service from the DiscoveryClient.
The default filter is rewrite path filter with the regex /serviceId/(?<remaining>.*) and the replacement
/${remaining}. This just strips the service id from the path before the request is sent
downstream.
If you would like to customize the predicates and/or filters used by the DiscoveryClient routes you can do so
by setting spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.predicates[x] and spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.filters[y].
When doing so you need to make sure to include the default predicate and filter above, if you want to retain
that functionality. Below is an example of what this looks like.
application.properties.
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.predicates[0].name: Path
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.predicates[0].args[pattern]: "'/'+serviceId+'/**'"
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.predicates[1].name: Host
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.predicates[1].args[pattern]: "'**.foo.com'"
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.filters[0].name: Hystrix
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.filters[0].args[name]: serviceId
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.filters[1].name: RewritePath
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.filters[1].args[regexp]: "'/' + serviceId + '/(?<remaining>.*)'"
spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.filters[1].args[replacement]: "'/${remaining}'"
The gateway can be configured to control CORS behavior. The "global" CORS configuration is a map of URL patterns to Spring Framework CorsConfiguration.
application.yml.
spring: cloud: gateway: globalcors: corsConfigurations: '[/**]': allowedOrigins: "http://docs.spring.io" allowedMethods: - GET
In the example above, CORS requests will be allowed from requests that originate from docs.spring.io for all GET requested paths.
The /gateway actuator endpoint allows to monitor and interact with a Spring Cloud Gateway application. To be remotely accessible, the endpoint has to be enabled and exposed via HTTP or JMX in the application properties.
application.properties.
management.endpoint.gateway.enabled=true # default value management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=gateway
To retrieve the global filters applied to all routes, make a GET request to /actuator/gateway/globalfilters. The resulting response is similar to the following:
{
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.LoadBalancerClientFilter@77856cc5": 10100,
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.RouteToRequestUrlFilter@4f6fd101": 10000,
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.NettyWriteResponseFilter@32d22650": -1,
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ForwardRoutingFilter@106459d9": 2147483647,
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.NettyRoutingFilter@1fbd5e0": 2147483647,
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ForwardPathFilter@33a71d23": 0,
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.AdaptCachedBodyGlobalFilter@135064ea": 2147483637,
"org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.WebsocketRoutingFilter@23c05889": 2147483646
}The response contains details of the global filters in place. For each global filter is provided the string representation of the filter object (e.g., org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.LoadBalancerClientFilter@77856cc5) and the corresponding order in the filter chain.
To retrieve the GatewayFilter factories applied to routes, make a GET request to /actuator/gateway/routefilters. The resulting response is similar to the following:
{
"[AddRequestHeaderGatewayFilterFactory@570ed9c configClass = AbstractNameValueGatewayFilterFactory.NameValueConfig]": null,
"[SecureHeadersGatewayFilterFactory@fceab5d configClass = Object]": null,
"[SaveSessionGatewayFilterFactory@4449b273 configClass = Object]": null
}The response contains details of the GatewayFilter factories applied to any particular route. For each factory is provided the string representation of the corresponding object (e.g., [SecureHeadersGatewayFilterFactory@fceab5d configClass = Object]). Note that the null value is due to an incomplete implementation of the endpoint controller, for that it tries to set the order of the object in the filter chain, which does not apply to a GatewayFilter factory object.
To clear the routes cache, make a POST request to /actuator/gateway/refresh. The request returns a 200 without response body.
To retrieve the routes defined in the gateway, make a GET request to /actuator/gateway/routes. The resulting response is similar to the following:
[{
"route_id": "first_route",
"route_object": {
"predicate": "org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.PathRoutePredicateFactory$$Lambda$432/1736826640@1e9d7e7d",
"filters": [
"OrderedGatewayFilter{delegate=org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.factory.PreserveHostHeaderGatewayFilterFactory$$Lambda$436/674480275@6631ef72, order=0}"
]
},
"order": 0
},
{
"route_id": "second_route",
"route_object": {
"predicate": "org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.PathRoutePredicateFactory$$Lambda$432/1736826640@cd8d298",
"filters": []
},
"order": 0
}]The response contains details of all the routes defined in the gateway. The following table describes the structure of each element (i.e., a route) of the response.
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | The route id. |
| Object | The route predicate. |
| Array | The GatewayFilter factories applied to the route. |
| Number | The route order. |
To retrieve information about a single route, make a GET request to /actuator/gateway/routes/{id} (e.g., /actuator/gateway/routes/first_route). The resulting response is similar to the following:
{
"id": "first_route",
"predicates": [{
"name": "Path",
"args": {"_genkey_0":"/first"}
}],
"filters": [],
"uri": "http://www.uri-destination.org",
"order": 0
}]The following table describes the structure of the response.
| Path | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | The route id. |
| Array | The collection of route predicates. Each item defines the name and the arguments of a given predicate. |
| Array | The collection of filters applied to the route. |
| String | The destination URI of the route. |
| Number | The route order. |
To create a route, make a POST request to /gateway/routes/{id_route_to_create} with a JSON body that specifies the fields of the route (see the previous subsection).
To delete a route, make a DELETE request to /gateway/routes/{id_route_to_delete}.
The table below summarises the Spring Cloud Gateway actuator endpoints. Note that each endpoint has /actuator/gateway as the base-path.
| ID | HTTP Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | Displays the list of global filters applied to the routes. |
| GET | Displays the list of GatewayFilter factories applied to a particular route. |
| POST | Clears the routes cache. |
| GET | Displays the list of routes defined in the gateway. |
| GET | Displays information about a particular route. |
| POST | Add a new route to the gateway. |
| DELETE | Remove an existing route from the gateway. |
TODO: overview of writing custom integrations
TODO: document writing Custom Route Predicate Factories
In order to write a GatewayFilter you will need to implement GatewayFilterFactory. There is an abstract class called AbstractGatewayFilterFactory which you can extend.
PreGatewayFilterFactory.java.
public class PreGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<PreGatewayFilterFactory.Config> { public PreGatewayFilterFactory() { super(Config.class); } @Override public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) { // grab configuration from Config object return (exchange, chain) -> { //If you want to build a "pre" filter you need to manipulate the //request before calling change.filter ServerHttpRequest.Builder builder = exchange.getRequest().mutate(); //use builder to manipulate the request return chain.filter(exchange.mutate().request(request).build()); }; } public static class Config { //Put the configuration properties for your filter here } }
PostGatewayFilterFactory.java.
public class PostGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<PostGatewayFilterFactory.Config> { public PostGatewayFilterFactory() { super(Config.class); } @Override public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) { // grab configuration from Config object return (exchange, chain) -> { return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse(); //Manipulate the response in some way })); }; } public static class Config { //Put the configuration properties for your filter here } }
In order to write a custom global filter, you will need to implement GlobalFilter interface. This will apply the filter to all requests.
Example of how to set up a Global Pre and Post filter, respectively
@Bean public GlobalFilter customGlobalFilter() { return (exchange, chain) -> exchange.getPrincipal() .map(Principal::getName) .defaultIfEmpty("Default User") .map(userName -> { //adds header to proxied request exchange.getRequest().mutate().header("CUSTOM-REQUEST-HEADER", userName).build(); return exchange; }) .flatMap(chain::filter); } @Bean public GlobalFilter customGlobalPostFilter() { return (exchange, chain) -> chain.filter(exchange) .then(Mono.just(exchange)) .map(serverWebExchange -> { //adds header to response serverWebExchange.getResponse().getHeaders().set("CUSTOM-RESPONSE-HEADER", HttpStatus.OK.equals(serverWebExchange.getResponse().getStatusCode()) ? "It worked": "It did not work"); return serverWebExchange; }) .then(); }
Spring Cloud Gateway provides a utility object called ProxyExchange which you can use inside a regular Spring web handler as a method parameter. It supports basic downstream HTTP exchanges via methods that mirror the HTTP verbs. With MVC it also supports forwarding to a local handler via the forward() method. To use the ProxyExchange just include the right module in your classpath (either spring-cloud-gateway-mvc or spring-cloud-gateway-webflux).
MVC example (proxying a request to "/test" downstream to a remote server):
@RestController @SpringBootApplication public class GatewaySampleApplication { @Value("${remote.home}") private URI home; @GetMapping("/test") public ResponseEntity<?> proxy(ProxyExchange<byte[]> proxy) throws Exception { return proxy.uri(home.toString() + "/image/png").get(); } }
The same thing with Webflux:
@RestController @SpringBootApplication public class GatewaySampleApplication { @Value("${remote.home}") private URI home; @GetMapping("/test") public Mono<ResponseEntity<?>> proxy(ProxyExchange<byte[]> proxy) throws Exception { return proxy.uri(home.toString() + "/image/png").get(); } }
There are convenience methods on the ProxyExchange to enable the handler method to discover and enhance the URI path of the incoming request. For example you might want to extract the trailing elements of a path to pass them downstream:
@GetMapping("/proxy/path/**") public ResponseEntity<?> proxyPath(ProxyExchange<byte[]> proxy) throws Exception { String path = proxy.path("/proxy/path/"); return proxy.uri(home.toString() + "/foos/" + path).get(); }
All the features of Spring MVC or Webflux are available to Gateway handler methods. So you can inject request headers and query parameters, for instance, and you can constrain the incoming requests with declarations in the mapping annotation. See the documentation for @RequestMapping in Spring MVC for more details of those features.
Headers can be added to the downstream response using the header() methods on ProxyExchange.
You can also manipulate response headers (and anything else you like in the response) by adding a mapper to the get() etc. method. The mapper is a Function that takes the incoming ResponseEntity and converts it to an outgoing one.
First class support is provided for "sensitive" headers ("cookie" and "authorization" by default) which are not passed downstream, and for "proxy" headers (x-forwarded-*).