Below you can find the answers to most frequently asked questions.
You can check the Jenkins logs and you’ll see
WARNING: Skipped parameter `PIPELINE_VERSION` as it is undefined on `jenkins-pipeline-sample-build`. Set `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.keepUndefinedParameters`=true to allow undefined parameters to be injected as environment variables or `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.safeParameters=[comma-separated list]` to whitelist specific parameter names, even though it represents a security breach
To fix it you have to do exactly what the warning suggests… Also ensure that the Groovy token macro processing
checkbox is set.
You can see that the Jenkins version is properly set but in the build version is still snapshot and
the echo "${PIPELINE_VERSION}" doesn’t print anything.
You can check the Jenkins logs and you’ll see
WARNING: Skipped parameter `PIPELINE_VERSION` as it is undefined on `jenkins-pipeline-sample-build`. Set `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.keepUndefinedParameters`=true to allow undefined parameters to be injected as environment variables or `-Dhudson.model.ParametersAction.safeParameters=[comma-separated list]` to whitelist specific parameter names, even though it represents a security breach
To fix it you have to do exactly what the warning suggests…
Docker compose, docker compose, docker compose… The problem is that for some reason, only in Docker, the execution of Java hangs. But it hangs randomly and only the first time you try to execute the pipeline.
The solution to this is to run the pipeline again. If once it suddenly, magically passes then it will pass for any subsequent build.
Another thing that you can try is to run it with plain Docker. Maybe that will help.
Sure! you can pass REPOS variable with comma separated list of
project_name$project_url format. If you don’t provide the PROJECT_NAME the
repo name will be extracted and used as the name of the project.
E.g. for REPOS equal to:
will result in the creation of pipelines with root names github-analytics and github-webhook.
E.g. for REPOS equal to:
foo$https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/github-analytics,bar$https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/atom-feed
will result in the creation of pipelines with root names foo for github-analytics
and bar for github-webhook.
Not really. This is an opinionated pipeline that’s why we took some
opinionated decisions like:
- usage of Spring Cloud, Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner and Spring Cloud Eureka
- application deployment to Cloud Foundry
For Maven:
- usage of Maven Wrapper
- artifacts deployment by
./mvnw clean deploy stubrunner.idsproperty to retrieve list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded- running smoke tests on a deployed app via the
smokeMaven profile - running end to end tests on a deployed app via the
e2eMaven profile
For Gradle (in the
github-analyticsapplication check thegradle/pipeline.gradlefile):- usage of Gradlew Wrapper
deploytask for artifacts deployment- running smoke tests on a deployed app via the
smoketask - running end to end tests on a deployed app via the
e2etask groupIdtask to retrieve group idartifactIdtask to retrieve artifact idcurrentVersiontask to retrieve the current versionstubIdstask to retrieve list of collaborators for which stubs should be downloaded
This is the initial approach that can be easily changed in the future.
Sure! It’s open-source! The important thing is that the core part of the logic is written in Bash scripts. That way, in the majority of cases, you could change only the bash scripts without changing the whole pipeline.
You must have pushed some tags and have removed the Artifactory volume that contained them. To fix this, just remove the tags
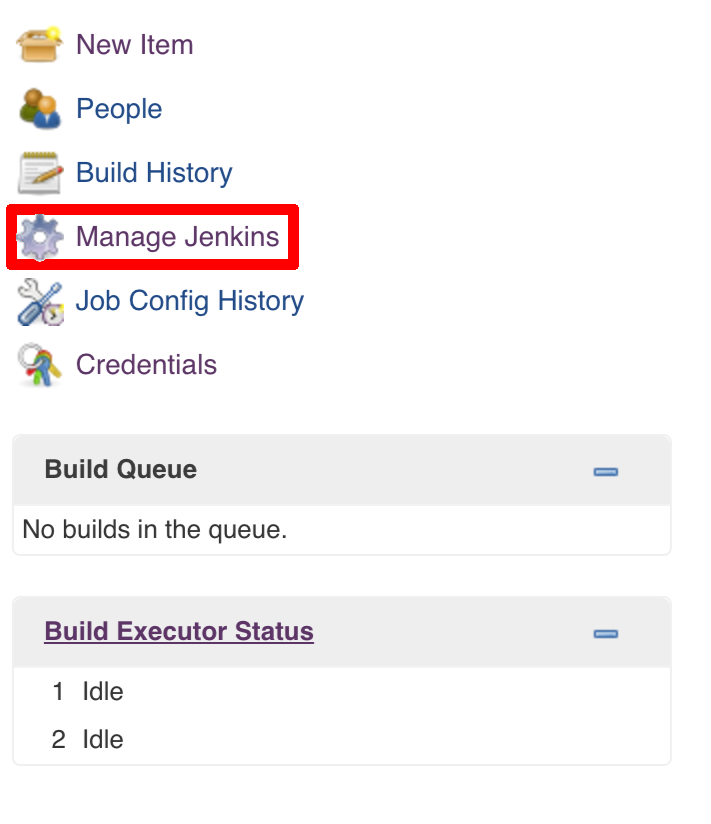
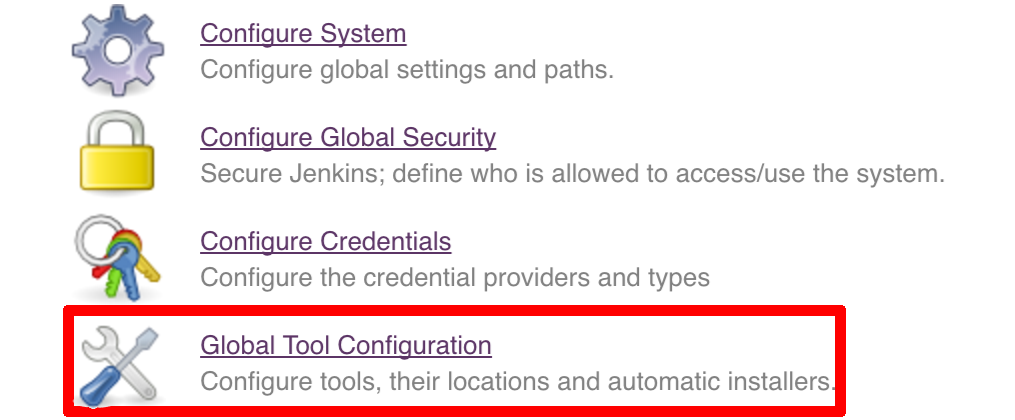
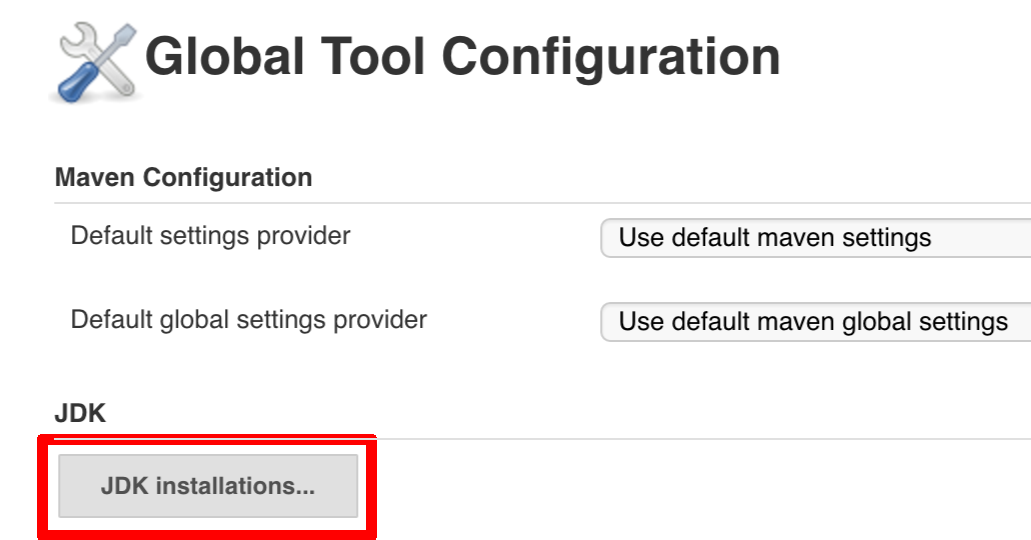
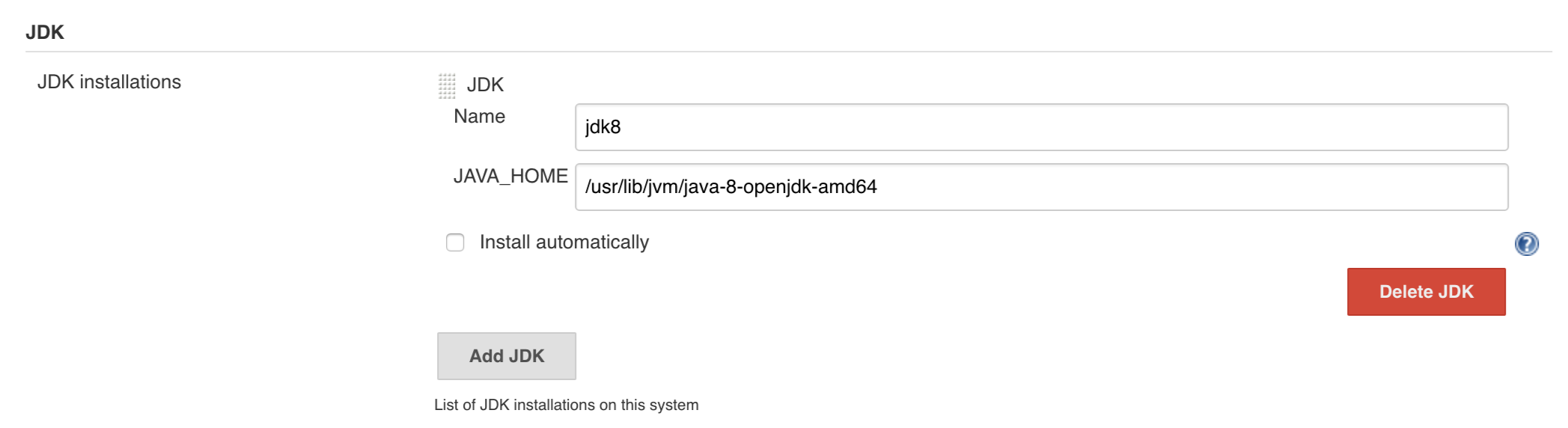
git tag -l | xargs -n 1 git push --delete origin- by default we assume that you have jdk with id
jdk8configured - if you want a different one just override
JDK_VERSIONenv var and point to the proper one
![[Tip]](images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
The docker image comes in with Java installed at |
To change the default one just follow these steps:
And that’s it!
With scripted that but if you needed to this manually then this is how to do it:
No problem, just set the property / env var to true
AUTO_DEPLOY_TO_STAGEto automatically deploy to stageAUTO_DEPLOY_TO_PRODto automatically deploy to prod
No problem, just set the API_COMPATIBILITY_STEP_REQUIRED env variable
to false and rerun the seed (you can pick it from the seed
job’s properties too).
When you get sth like this:
19:01:44 stderr: remote: Invalid username or password. 19:01:44 fatal: Authentication failed for 'https://github.com/marcingrzejszczak/github-webhook/' 19:01:44 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl.launchCommandIn(CliGitAPIImpl.java:1740) 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl.launchCommandWithCredentials(CliGitAPIImpl.java:1476) 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl.access$300(CliGitAPIImpl.java:63) 19:01:44 at org.jenkinsci.plugins.gitclient.CliGitAPIImpl$8.execute(CliGitAPIImpl.java:1816) 19:01:44 at hudson.plugins.git.GitPublisher.perform(GitPublisher.java:295) 19:01:44 at hudson.tasks.BuildStepMonitor$3.perform(BuildStepMonitor.java:45) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.AbstractBuild$AbstractBuildExecution.perform(AbstractBuild.java:779) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.AbstractBuild$AbstractBuildExecution.performAllBuildSteps(AbstractBuild.java:720) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.Build$BuildExecution.post2(Build.java:185) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.AbstractBuild$AbstractBuildExecution.post(AbstractBuild.java:665) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.Run.execute(Run.java:1745) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.FreeStyleBuild.run(FreeStyleBuild.java:43) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.ResourceController.execute(ResourceController.java:98) 19:01:44 at hudson.model.Executor.run(Executor.java:404)
most likely you’ve passed a wrong password. Check the credentials section on how to update your credentials.
Most likely you’ve forgotten to update your local settings.xml with the Artifactory’s
setup. Check out this section of the docs and update your settings.xml.
In some cases it may be required that when performing a release that the artifacts be signed
before pushing them to the repository.
To do this you will need to import your GPG keys into the Docker image running Jenkins.
This can be done by placing a file called public.key containing your public key
and a file called private.key containing your private key in the seed directory.
These keys will be imported by the init.groovy script that is run when Jenkins starts.
The seed job checks if an env variable GIT_USE_SSH_KEY is set to true. If that’s the case
then env variable GIT_SSH_CREDENTIAL_ID will be chosen as the one that contains the
id of the credential that contains SSH private key. By default GIT_CREDENTIAL_ID will be picked
as the one that contains username and password to connect to git.
You can set these values in the seed job by filling out the form / toggling a checkbox.
There can be a number of reason but remember that for stage we assume that a sequence of manual steps need to be performed. We don’t redeploy any existing services cause most likely you deliberately have set it up in that way or the other. If in the logs of your application you can see that you can’t connect to a service, first ensure that the service is forwarding traffic to a pod. Next if that’s not the case please delete the service and re-run the step in the pipeline. That way Spring Cloud Pipelines will redeploy the service and the underlying pods.
[jenkins-cf-resources]] When deploying the app to stage or prod you can get an exception Insufficient resources. The way to
solve it is to kill some apps from test / stage env. To achieve that just call
cf target -o pcfdev-org -s pcfdev-test
cf stop github-webhook
cf stop github-eureka
cf stop stubrunnerYou can also execute ./tools/cf-helper.sh kill-all-apps that will remove all demo-related apps
deployed to PCF Dev.
If you receive a similar exception:
20:26:18 API endpoint: https://api.local.pcfdev.io (API version: 2.58.0) 20:26:18 User: user 20:26:18 Org: pcfdev-org 20:26:18 Space: No space targeted, use 'cf target -s SPACE' 20:26:18 FAILED 20:26:18 Error finding space pcfdev-test 20:26:18 Space pcfdev-test not found
It means that you’ve forgotten to create the spaces in your PCF Dev installation.
If you play around with Jenkins / Concourse you might end up with the routes occupied
Using route github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io Binding github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io to github-webhook... FAILED The route github-webhook-test.local.pcfdev.io is already in use.
Just delete the routes
yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n stubrunner-test yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-stage yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-stage yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-webhook-prod yes | cf delete-route local.pcfdev.io -n github-eureka-prod
You can also execute the ./tools/cf-helper.sh delete-routes
Assuming that you’re already logged into the cluster it’s enough to run the
helper script with the REUSE_CF_LOGIN=true env variable. Example:
REUSE_CF_LOGIN=true ./tools/cf-helper.sh setup-prod-infra
This script will create the mysql db, rabbit mq service, download and deploy Eureka to the space and organization you’re logged into.